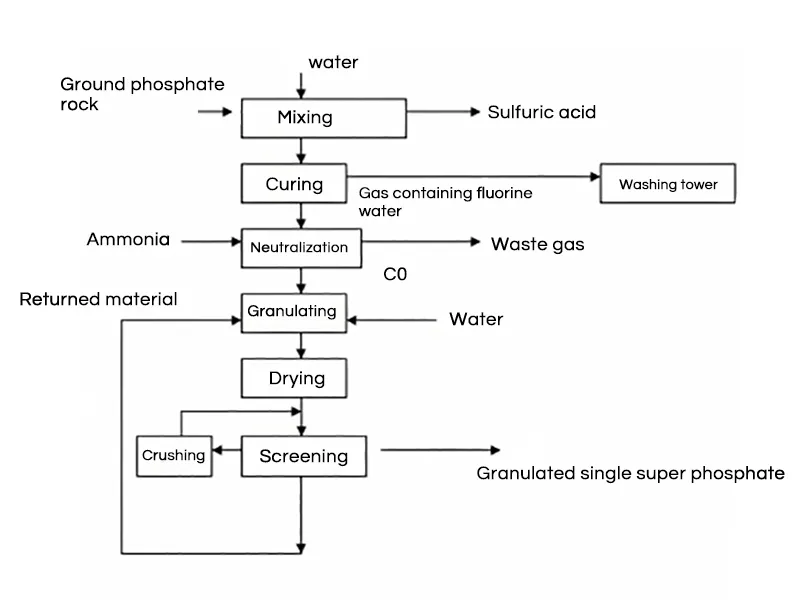
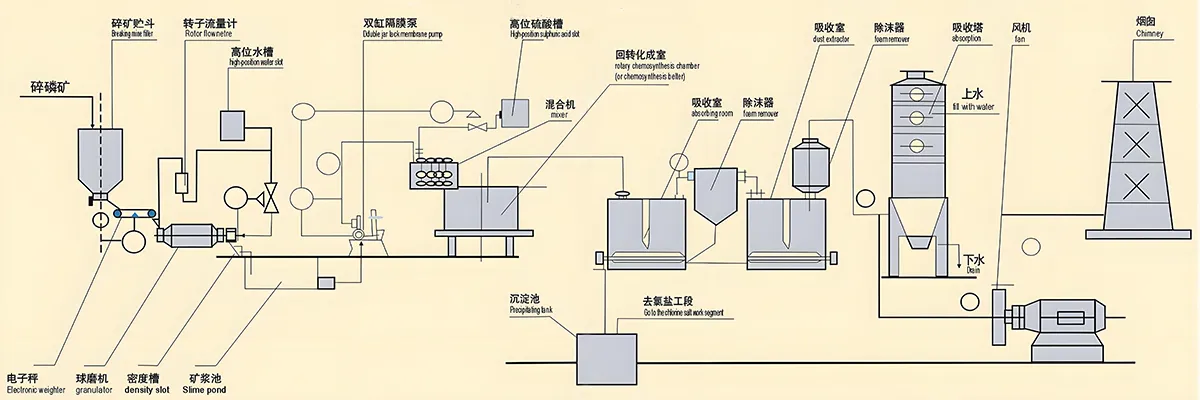
Process Features
- Better nutrient absorption
Granulated SSP is less reactive with the soil compared to its powdered form, making nutrients more readily available for plant uptake and improving overall fertilizer effectiveness.
- Minimized phosphorus loss
By reducing the contact area between the phosphorus in the fertilizer and the soil, granulated SSP helps prevent the phosphorus from being "locked up" in the soil, ensuring that more of it is available for crops.
- Simplified application
The granular format of SSP is easier to spread using mechanized equipment, making it more efficient and convenient for large-scale agricultural operations.
- Improved product quality
Through precise drying and cooling, the granules develop a more consistent shape and size, enhancing the product’s visual appeal and making it more competitive in the market.
- Environmental safeguards
The fertilizer production process incorporates effective waste gas treatment systems to minimize the environmental impact, keeping the production eco-friendly.
- Strict quality assurance
Quality checks at every stage of production ensure that the final product consistently meets high standards, providing reliable results for farmers.
- Efficient use of resources
By recycling and reusing by-products and waste materials generated during production, the process maximizes resource efficiency and reduces waste.
- Flexible production
The production line can be adjusted to produce different quantities and specifications of SSP, allowing manufacturers to respond easily to changes in market demand.
- Adaptable to raw materials
The process is designed to handle phosphate rock from various sources and of different qualities, making it versatile and adaptable to different raw materials.
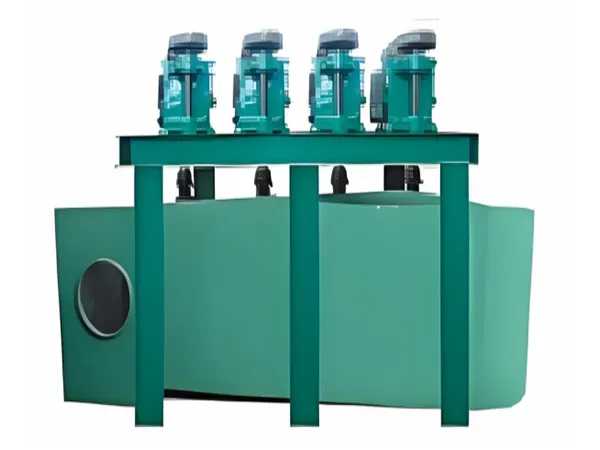
Main Equipment
Vertical Multiple Paddle Mixer
| Model | Paddle number | Effective volume (m³) | Production capacity (t/h) | Motor model | Power (kW) |
| 4LH3200×1200×924 | 4 | 0.8 | 3-4 | Y132M2-6 | 5.5*4 |
| 4LH3700×1200×925 | 4 | 1.32 | 5-7 | Y160L-6
Y160L-8 | 11*2 |
| 4LH3200×1200×926 | 4 | 3.2 | 12-14 | Y180L-6 | 15*4 |
| 4UH5600×1020×1100 | 4 | 4.5 | 24-27 | Y20001-6 | 5.8*4 |
| 4LH4450×1000×123 | 4 | 2.935 | 24-27 | Y20001-6 | 5.9*4 |
| 4UH3690×1336×1218 | 3 | 2.26 | 27-30 | Y200L2-6 | 5.1*4 |
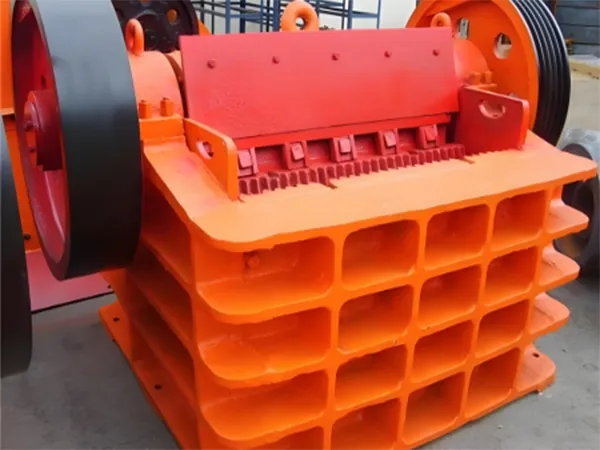
Jaw Crusher
| Model | Max. feeding size (mm) | Average final size | Processing capacity (t/h) | Weight (without motor) (kg) |
| PEX150×750A | 120 | 6-8 | 10-40 | 3000 |
| PEX150×1000A | 120 | 8-10 | 15-50 | 6000 |
| PEX250×400 | 210 | 20-80 | 5-20 | 2700 |
| PEX400×600 | 350 | 40-100 | 17-115 | 6428 |
| PEX600×900 | 350 | 75-200 | 56-192 | 17625 |
| PEX250×1000A | 210 | 10-15 | 10-30 | 6500 |
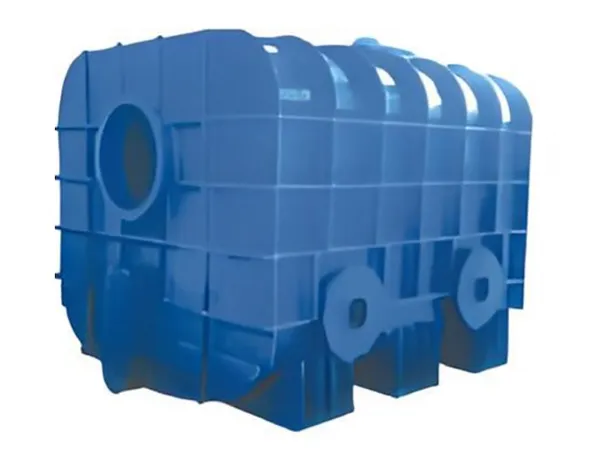
Fluorine Absorbing Unit
| Model | Belt speed (r/m) | Production capacity (10,000 tons/year) | Motor power (kW) |
| B1200×24000 | 0.015/0.045 | 3 | 7.5 |
| B1400×45000 | 0.015/0.045 | 10 | 7.5 |
| B1400×45000 | 0.015/0.045 | 20 | 11 |
Rotary Chemical Synthesis Chamber
| Model | Effective volume (m³) | Rotation speed (rpm) | Motor power (kW) |
| Ø2800×1800 | 8.43 | 35.6 | 4 |
| Ø3500×2000 | 10 | 60 | 7.5 |
| Ø5000×2200 | 20 | 73 | 7.5 |
| Ø7000x2200 | 55 | 70.15 | 15 |