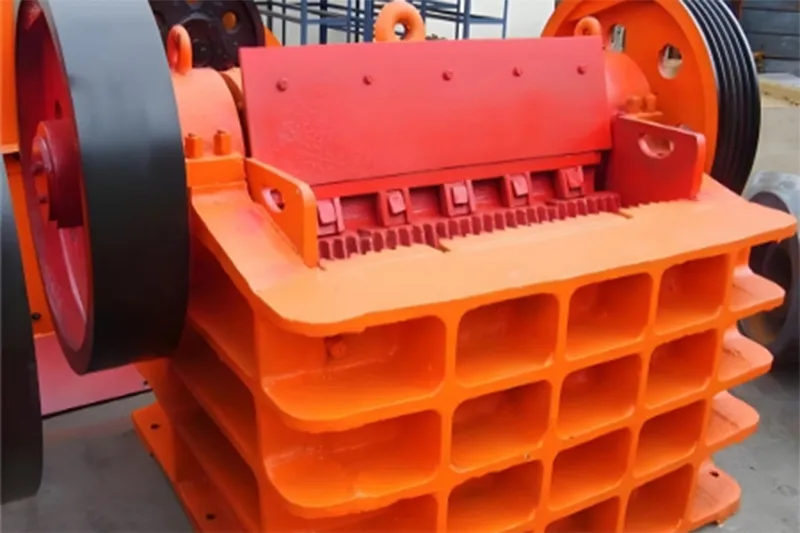
In fertilizer production, drying and cooling machines are important components to ensure the proper handling of materials. These drying machines use heat generated from coal or natural gas, which is then circulated through the dryer by fans to remove moisture from the material quickly. Once the drying process is complete, the cooling machine takes over, reducing the temperature of the product to a level suitable for packaging. This two-step process helps stabilize the fertilizer and guarantees it can be safely stored and transported without compromising quality.
-
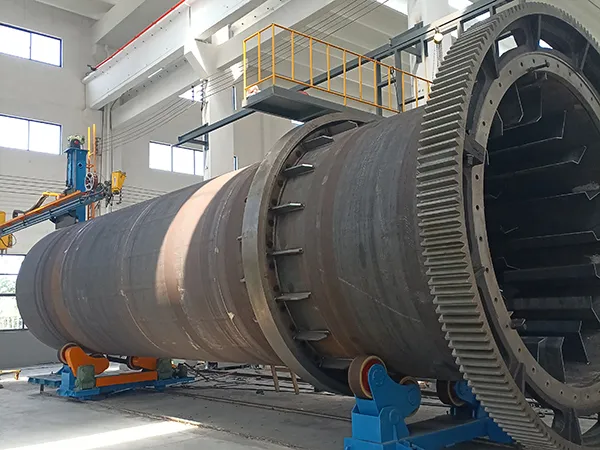

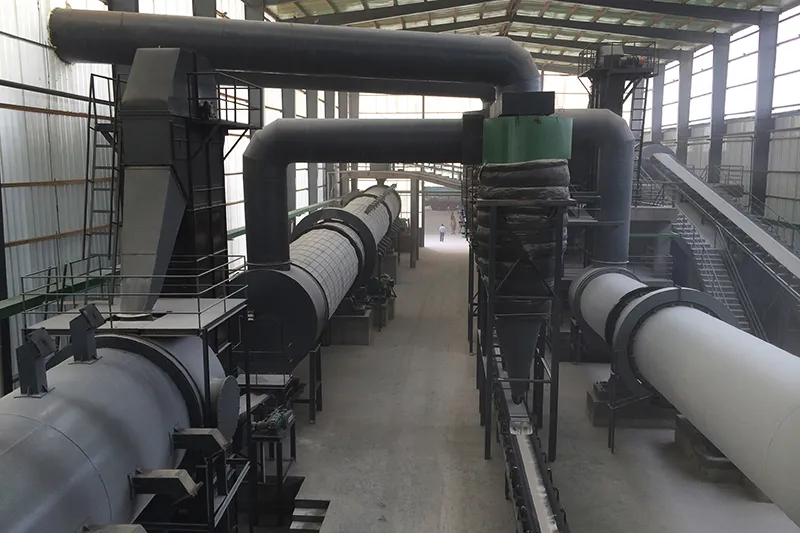
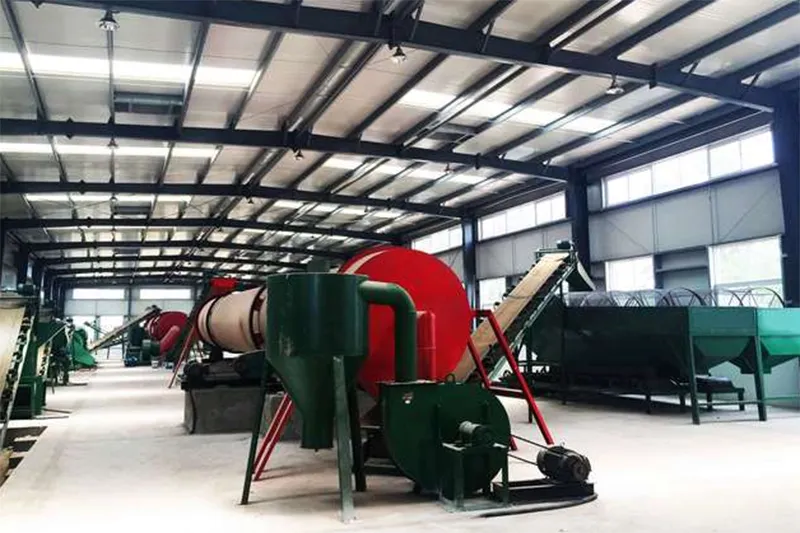
- Rotary Dryer The rotary dryer operates by introducing heated air while the inclined drum continuously rotates, allowing wet materials to move forward and exchange heat effectively with the air. Widely used in agriculture, chemicals, and mining, it caters to various production scales and material types.
- Constructed with a high-precision ground base, offering high concentricity and reduced wear, resulting in longer operational life.
- The drum features flange connections, ensuring precise alignment and easy maintenance or replacement.
-
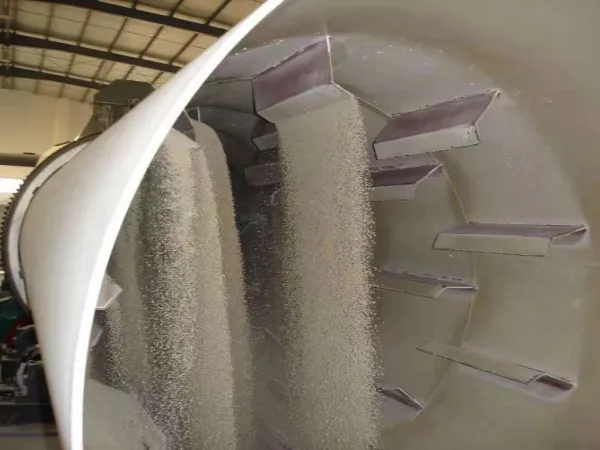

- Rotary Cooler Rotary coolers are used in various industries, including fertilizers, cement, and metallurgy, designed for efficiently cooling high-temperature materials. The rotary cooling machine operates by rotating its drum at an incline, allowing hot materials to move forward while simultaneously coming into contact with ambient air. This interaction not only cools the material but also helps evaporate moisture, increasing the strength of granules.
- The rotary cooler’s drum is processed using a ground-based lathe, ensuring precise concentricity, which minimizes wear and reduces energy consumption.
- The drum is connected using high-precision flanges, allowing for easy maintenance and part replacement.
What are the main stages in fertilizer production?
Drum granulation:
- Gathering raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other essential minerals
- Mixing and blending the materials thorough
- Heating and processing the mixture to form granules
- Drying and cooling the granulated product to prepare for packaging
Extrusion granulation:
- Drying the raw mixture and grinding it into a fine powder
- Pressing the powder into granules
- Screening the granules to ensure uniformity